Molecular Physics
The Grand Unified Theory of Classical Physics – Molecular Theory Resources

A Brilliant Light Power subsidiary, Millsian, Inc, has developed a molecular modeling tool based on The Grand Unified Theory of Classical Physics. Download a free trial of Millsian software.
View the Molecular Physics Slideshow (PDF)
View the book: Volume 2: Molecular Physics.
View accompanying spreadsheets:
Alkali F and Cl
Alkali Hydrides
Alkali Metals
Alkyl Aluminum
Amino Acids
Aspirin
Boron Functional Groups
Carbon Allotropes
Condensed Matter Physics
Di and Poly Atomic Molecules
DNA Functional Groups
Ge, Pb, As, Sb, Bi Functional Groups
H2+ and H2 Excited States
H2+ H2 Folder
RDX
Silicon Functional Groups
Tin
Transition Metal Coordinate Compounds and Organometallics
Molecules and Functional Groups Archive (ZIP, 9.2MB)
Complete collection of Excel files (1,600+ files) used to solve molecules and functional groups using the GUT-CP.
Bond Angles Archive (ZIP, 2MB)
Complete collection of Excel files (900+ files) used to solve bond angles (to first approximation) using the GUT-CP.
Bond Moments Archive (ZIP, 265KB)
Collection of Excel files used to solve bond moments of major set of functional groups.
View Summary Tables:
Molecular Summary Tables (PDF)
Molecules Solved by Millsian Compared to Experimental Values.
Partial List of Organic Functional Groups Solved by Classical Physics (PDF)
Partial List of Additional Molecules and Compositions of Matter Solved by Classical Physics (PDF)
View Related Papers:
Total Bond Energies of Exact Classical Solutions of Molecules Generated by Millsian 1.0 Compared to Those Computed Using Modern 3-21G and 6-31G* Basis Sets – R.L. Mills, B. Holverstott, W. Good, N. Hogle, A. Makwana – 07/23/09
Millsian 2.0: A Molecular Modeling Software for Structures, Charge Distributions and Energetics of Biomolecules, W. Xie, R.L. Mills, W. Good, A. Makwana, B. Holverstott, N. Hogle, Physics Essays, 24 (2011) pp. 200-212.
The Nature of the Chemical Bond Revisited and an Alternative Maxwellian Approach – R.L. Mills, Physics Essays, Vol. 17, No. 3, September (2004), pp. 342-389.
View accompanying spreadsheets.
View Related Visualizations:
View the Examples of Molecules page on the Millsian Website.
This program allows the user to numerically calculate and render the charge distribution profile and angular momentum projections of the hydrogen atom, both unnormalized and normalized.
This program allows the user to numerically calculate and render the ellipsoidal charge distribution profile of the hydrogen molecular orbital that uses a prolate ellipsoidal transform of the H atom current that conserves angular moment. This program may not run properly on all systems.
Molecules
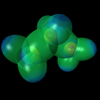
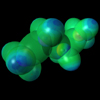
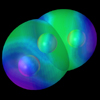
below: In molecules, a prolate spheroidal electron atomic orbital surrounds two nuclei, which are at the foci. The charge density increases nearer the foci, decreasing the total energy of the system.
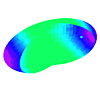 Hydrogen Molecule Hydrogen Molecule(See Fig. 11.5) view animation |
||
Reaction Sequences
|
left: Dynamic visualization of chloromethane (CH3Cl) receiving a chloride ion to become the Cl-CH3Cl bound complex, then the Cl.CH3.Cl transition state, then back to the bound complex, and once again to chloromethane, releasing a chloride ion.
|
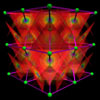
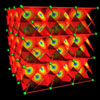
Extended Solids
below: In metals, the electron planes behave as mirror-image negative point charges to the positive ions such that the metallic crystal lattice bonding is Coulombic in the same way as that of an ionic compound. In a semiconductor, the electron planes carry the conducting current through the lattice. In a superconductor, the electron planes are uninhibited through the lattice.
|
|